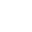
Thermal Printing Methods: Direct Thermal vs. Thermal Transfer
Thermal Barcode Printers are invaluable tools across industries like food service, retail, and healthcare, where labeling is critical for product identification, inventory management, and regulatory compliance.
Two primary thermal printing technologies—direct thermal printing and thermal transfer printing—are commonly used for creating thermal labels.
A
Thermal Printer uses direct heat to print on heat-sensitive paper, creating images without ink or ribbons. It’s typically faster and simpler but limited to printing on special thermal paper.
A
thermal Transfer Printer, on the other hand, uses heat to transfer ink from a ribbon onto various materials (such as paper, plastic, or fabric), offering more versatility and durability in prints, especially for labels or barcodes.
While both methods provide high-quality printing, the choice between them depends on the specific application and durability requirements.
1.How it works:
Direct Thermal Printing
Direct thermal printing uses heat to print on thermal paper, which is chemically treated to darken when exposed to heat.
A thermal printhead applies heat directly to the thermal paper to produce the image, text, or barcode.
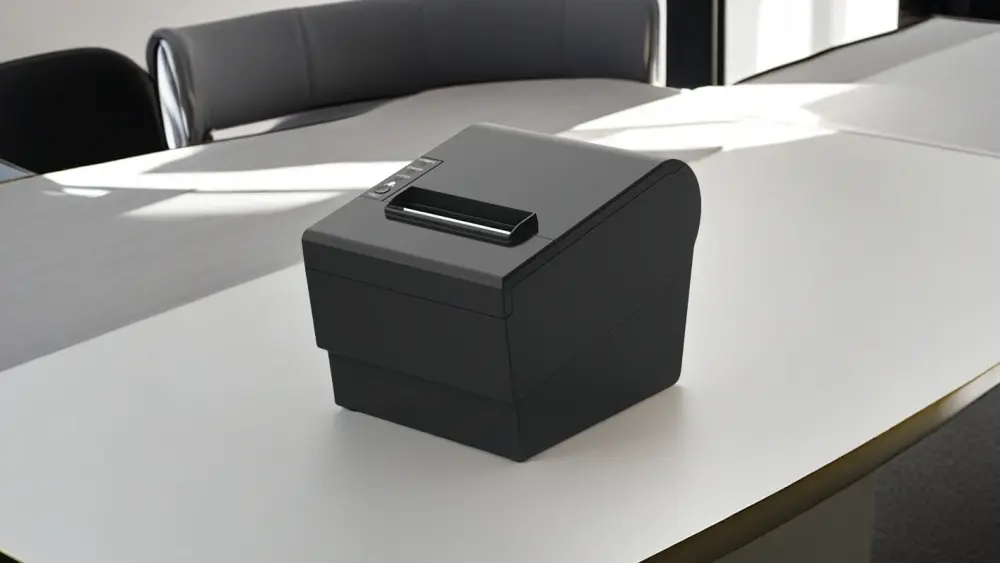

Thermal Printer
Thermal Transfer Printing
Thermal transfer printing uses a heat-sensitive ribbon (typically wax, resin, or a combination of both) that is heated by the printhead. The heat melts the ink from the ribbon and transfers it onto the surface of the label material.
This method allows printing on a wider range of materials (such as paper, plastic, fabric, and synthetic materials) beyond just thermal paper.
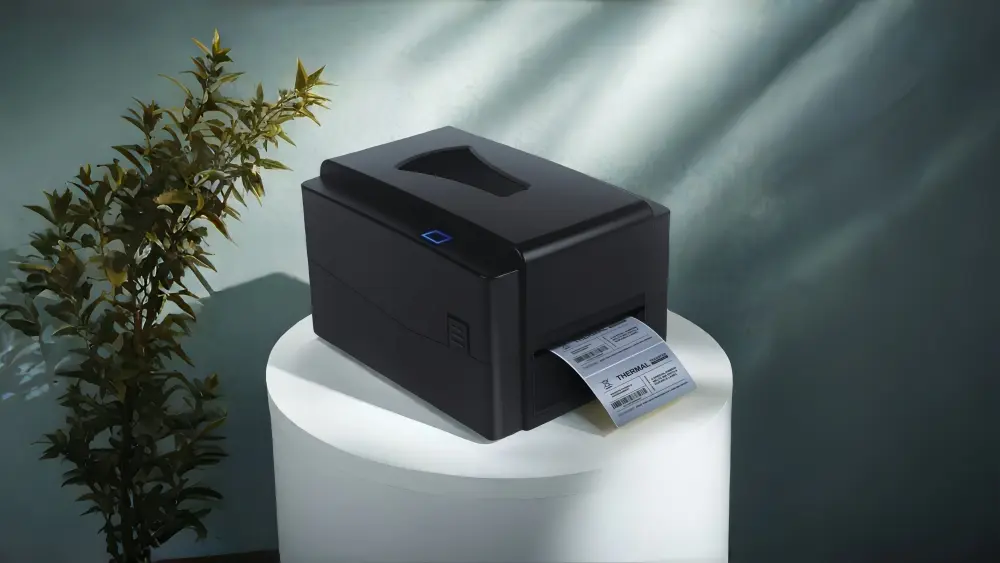

Thermal Transfer Printer
2.Advantages:
Direct Thermal Printing
No ink, toner, or ribbon required: Since the heat directly alters the paper, no consumables are needed other than the special thermal paper.
Simpler and lower maintenance: With fewer moving parts, direct thermal printers require less maintenance and are generally simpler to operate.
Cost-effective: Without the need for ink or ribbon, the overall printing cost is lower.
Fast printing speed: Direct thermal printing can be quicker than thermal transfer due to its simpler process.
Compact design: These printers are often smaller, making them ideal for mobile applications and limited spaces.
Thermal Transfer Printing
Durability: Thermal transfer prints are much more durable than direct thermal prints, resistant to fading, scratches, smudges, and chemicals. The prints are ideal for labels that need to withstand extreme conditions, including exposure to sunlight, humidity, and abrasion.
Versatile media options: Thermal transfer printing can be done on a variety of materials, including synthetic, polyester, and fabric-based media, which makes it ideal for applications that require specialized or high-performance labels.
Longer-lasting labels: The prints are highly resistant to environmental factors, making them more suitable for items that need to be tracked over longer periods (e.g., barcodes, asset tracking, and product labeling).
3.Disadvantages:
Direct Thermal Printing
Limited durability: The printed text or image can fade over time, especially when exposed to heat, light, or abrasion. This makes direct thermal printing unsuitable for long-term labeling needs.
Can only use thermal paper: The type of material used for direct thermal printing is restricted to thermal paper, which limits its versatility for different label types.
Not ideal for outdoor use: Labels may not be resistant to harsh environmental conditions such as humidity, oils, or chemicals.
Thermal Transfer Printing
Additional consumables: Thermal transfer printers require ribbons, which increases operational costs compared to direct thermal printing.
Slower than direct thermal: Because of the ribbon and additional steps in the process, thermal transfer printing is generally slower than direct thermal printing.
Higher initial investment: Thermal transfer printers tend to have a higher upfront cost due to the need for additional components (e.g., ribbons, more advanced printheads).
4.Best for:
Direct Thermal Printing
Short-term or disposable labels
Retail, shipping, and warehouse applications
Price tags, receipts, and event tickets
Applications where durability is not a critical factor
Thermal Transfer Printing
Long-lasting labels and high-durability applications
Asset management, inventory tracking, and product labeling
Outdoor, industrial, or warehouse labeling applications where exposure to the elements is common
Applications that require the use of specialized label materials
5.Key Differences Between Direct Thermal and Thermal Transfer Printing
Feature | Direct Thermal Printing | Thermal Transfer Printing |
Printing Process | Direct heat on thermal paper | Heat transfers ink from ribbon to label material |
Durability | Prints fade over time, not ideal for long-term use | Prints are highly durable and long-lasting |
Media Type | Can only print on thermal paper | Can print on various materials (paper, synthetic, fabric, etc.) |
Ink/Ribbon Requirement | No ribbon or ink required | Requires ink ribbon (wax, resin, or mixed) |
Speed | Faster printing | Slower due to additional process steps |
Cost | Generally lower cost (no ribbons needed) | Higher operational cost (ribbons needed) |
Maintenance | Lower maintenance, fewer components | More components, potentially higher maintenance |
Applications | Short-term labels, receipts, shipping, etc. | Long-term labeling, asset tracking, product identification |
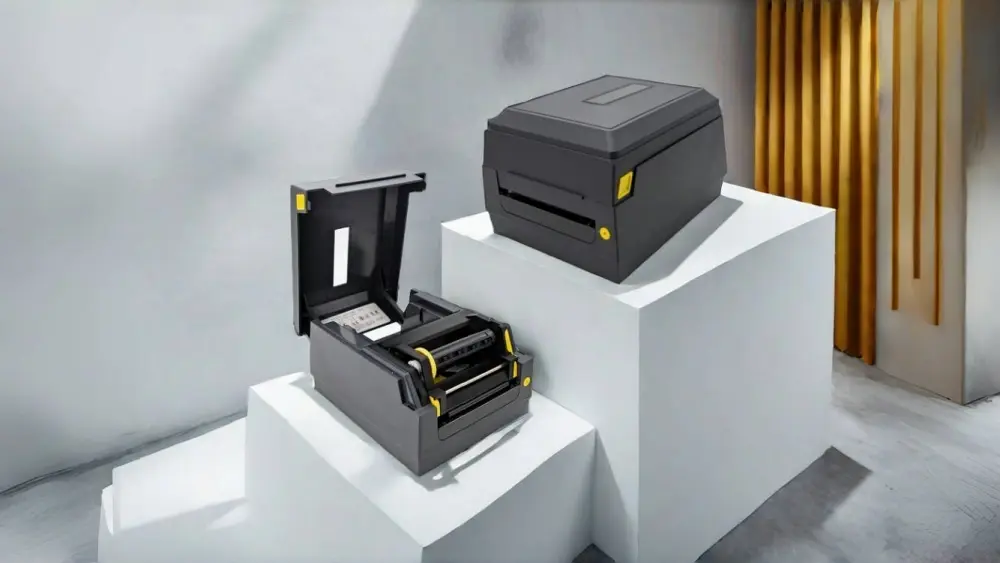

Thermal Heat Transfer Printer with Ribbon
6.Which One Should You Choose?
For short-term, cost-effective labeling where durability is not critical (such as price tags, shipping labels, or receipts), direct thermal printing is a great option. It’s fast, inexpensive, and easy to maintain.
For long-lasting labels that need to withstand environmental conditions (e.g., warehouse tags, barcodes, inventory labels), thermal transfer printing is the better choice. It offers higher print durability and versatility for a wide range of materials, making it suitable for industrial and outdoor applications.
7.Conclusion
Both direct thermal and thermal transfer printing methods have distinct advantages depending on the application. Direct thermal printing is an ideal solution for temporary labels that don't need to endure harsh conditions, while thermal transfer printing excels in creating durable, long-lasting labels that can withstand exposure to various environmental factors.
Carefully consider your labeling needs in terms of durability, material compatibility, and cost before deciding on the right thermal printing method for your business.
Whether you need the thermal printer or thermal transfer printer, please feel free to contact us--Xiamen OPOS Printer
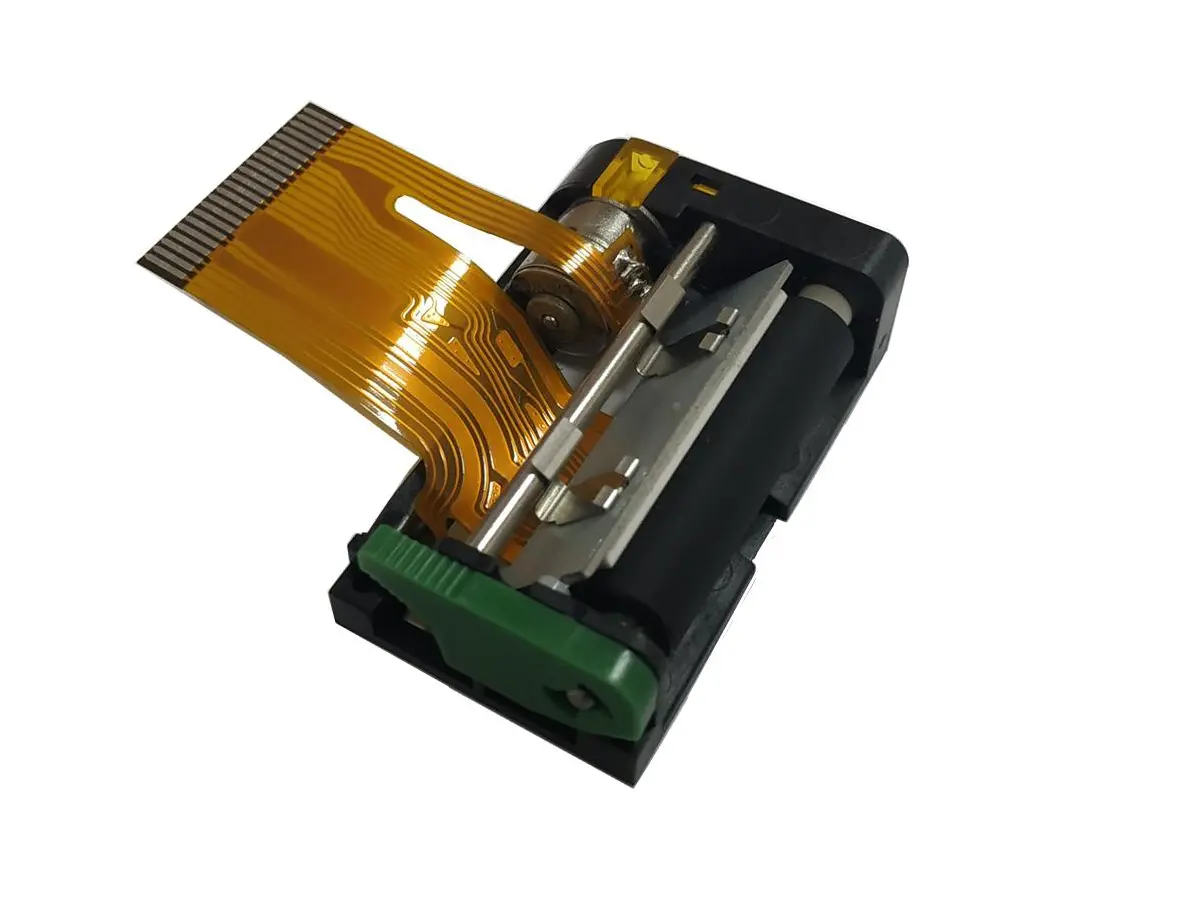



 1 inch thermal printer mechanism
1 inch thermal printer mechanism 2 inch thermal printer mechanism
2 inch thermal printer mechanism 3 inch thermal printer mechanism
3 inch thermal printer mechanism 4 inch thermal printer mechanism
4 inch thermal printer mechanism 8 inch thermal printer mechanism
8 inch thermal printer mechanism dot matrix printer mechanism
dot matrix printer mechanism Label Printer
Label Printer Receipt Printer
Receipt Printer Mobile Printer
Mobile Printer