In today's fast-paced retail environment, a Barcode Thermal Printer has become essential. According to Mark Johnson, an industry expert, "These printers streamline processes and enhance efficiency." His words highlight the impact that these devices have on various sectors. From inventory management to point-of-sale systems, a Barcode Thermal Printer delivers accuracy and speed.
These printers use heat to transfer ink onto labels, producing crisp and durable barcodes. The technology is simple yet effective, making it widely adopted. However, not all printers are created equal. Some businesses face challenges with label durability and print quality. Reflection on these issues can lead to better operational decisions.
As retail and logistics grow increasingly complex, the demand for Barcode Thermal Printers continues to rise. These machines are vital for maintaining organization and workflow. Yet, companies must carefully evaluate their printer choice to avoid inefficiencies in the long run. Emphasizing quality will result in improved performance and satisfaction.

Barcode thermal printers are essential tools in various industries. They create high-quality barcode labels using heat-sensitive materials. This method speeds up the printing process and often reduces costs. According to a recent market report, the global demand for these printers is expected to grow by 5.2% annually, reaching a value of over $1.5 billion by 2026.
Common uses include retail, logistics, and healthcare. In retail, these printers help track inventory with precise barcodes. In logistics, they simplify package tracking and delivery. The healthcare sector benefits greatly by ensuring accurate medication administration through barcode labeling. However, users sometimes face challenges with printer compatibility and software integration. This can lead to delays and frustration, especially during peak operational hours.
Thermal printers also have limitations concerning label durability. While they create sharp images, exposure to heat and sunlight can cause fading. Many users overlook maintenance, which can lead to print quality issues. These factors should be addressed for optimal performance. The right care can extend the life of these printers significantly.
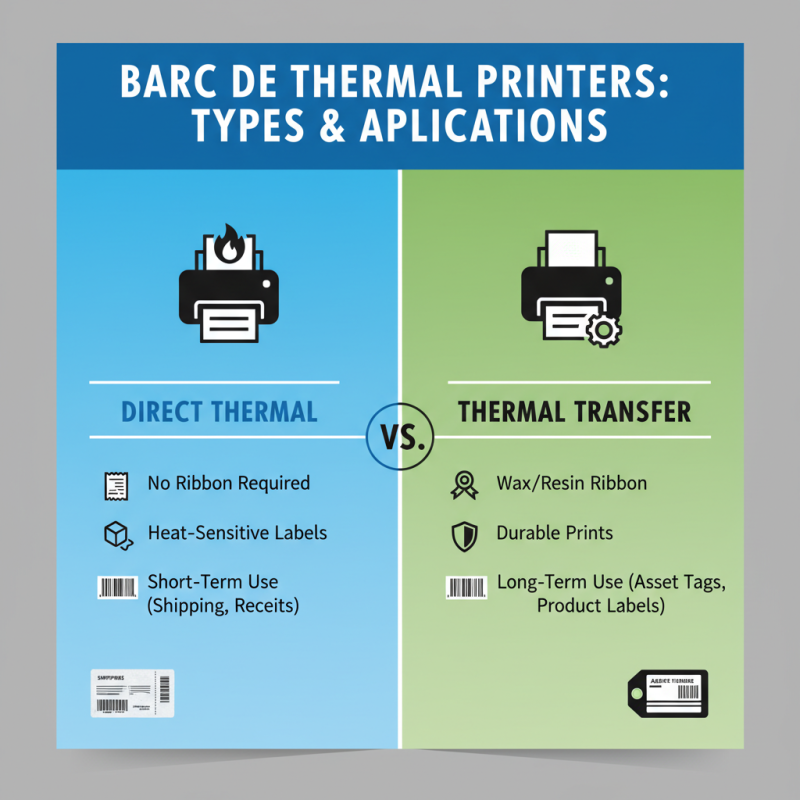
Barcode thermal printers come in two main types: direct thermal and thermal transfer. Each one has unique characteristics that suit different applications.
Direct thermal printers use special heat-sensitive paper. When the print head heats certain areas, the paper turns black. This type is efficient for creating short-lived labels. It’s common in shipping and receipts. However, the printed labels can fade over time, especially when exposed to heat or sunlight. This limitation can be a drawback for products needing long-lasting labeling.
Thermal transfer printers, on the other hand, use a ribbon to transfer ink onto the label. The print head heats the ribbon, and ink adheres to the label surface. This method creates stronger and more durable prints. It’s ideal for industries that need labels to resist fading or scratching. Yet, the ribbons can be costly, and users must manage supplies carefully. Sometimes, the complexity of switching ribbons can lead to downtime, which can be frustrating.
Barcode thermal printers are essential tools in various industries. They operate using two main technologies: direct thermal and thermal transfer printing. In direct thermal printing, heat-sensitive paper reacts to heat from the printer. This method produces clear images without needing ink or ribbons. However, this method may fade over time.
Thermal transfer printing, on the other hand, uses a ribbon coated with ink. The printer heats the ribbon, transferring ink onto the label. This method results in more durable prints that can withstand heat and sunlight. Both methods have their pros and cons. Users must consider their specific needs before choosing a printing method.
Tips: Regular maintenance is critical. Dust and debris can affect print quality. Always check ribbon and paper compatibility. This avoids common printing issues. Sometimes, simple mistakes can lead to significant problems in labeling. Design your barcode carefully; poor sizing can make scanning difficult.
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Print Head | The component that applies heat to the thermal paper to create images. | Transfers inkless thermal images onto the substrate. |
| Thermal Paper | Specially coated paper that changes color when heated. | Serves as the medium for the printed barcode. |
| Control Board | The electronic circuit that manages the printer's operation. | Processes data and controls the print head's heating cycle. |
| Power Supply | Provides the necessary power to the printer's components. | Ensures reliable operation and print quality. |
| Interface Ports | Connection points for data transfer from the computer to the printer. | Facilitates communication between devices. |
Barcode thermal printers play a significant role in enhancing inventory management efficiency. In warehouses and retail environments, quick access to accurate data is crucial. Studies show that companies can reduce inventory errors by up to 30% when implementing barcode systems. This improvement stems from the speed and accuracy these printers offer. They create high-quality barcodes that can be scanned rapidly, minimizing human error.
These printers work by applying heat to thermal paper, generating clear barcodes that can be easily read. When items are scanned at checkout or during stock checks, data flows seamlessly into inventory systems. According to a report from TechValidate, 74% of businesses noted a considerable reduction in stock discrepancies with barcode tech. This shift allows for real-time inventory tracking, which aids in decision-making and reduces holding costs.
However, some organizations struggle with adoption. Still, transitioning to a barcode system is worth considering. Challenges like staff training and system integration often arise. Addressing these hurdles can lead to improved accuracy and efficiency in inventory management. Investing in this technology might require time and resources, but the benefits often outweigh these initial difficulties.
Print resolution in barcode thermal printing is critical. It determines how clearly the barcode is printed. A higher resolution leads to sharper prints. This clarity helps scanners read barcodes effectively. Common resolutions range from 203 to 600 DPI. The right resolution depends on the application's needs. For example, small labels may need higher DPI. Conversely, large labels may work well at lower DPI. Misalignment can occur if resolution is too high for the label size.
Speed is equally important in barcode printing. It's measured in inches per second (IPS). Some printers can produce labels quickly, about 6 IPS or more. This speed is vital for high-volume environments. Delays can create bottlenecks. However, speed can sometimes lead to errors. When printing too fast, barcodes may be misprinted or unreadable. Balancing speed and print quality is essential. Users often need to adjust settings based on their workflow. Finding the right compromise can be a challenge. Test runs can help identify the optimal settings.






